What is kinematic viscosity?
The kinematic viscosity [m2/s] is the ratio between the dynamic viscosity [Pa.s = 1 kg/m·s] and the density of a fluid [kg/m3].
The SI unit of the kinematic viscosity is m2/s. Other units are: 1 St (Stoke) = 1 cm2/s = 10−4 m2/s. 1 cSt (centiStoke) = 1 mm2/s = 10−6m2/s.
Water at 20 °C has a kinematic viscosity of about 1 cSt.
One way is to measure a fluid’s resistance to flow when an external force is applied. This is dynamic viscosity.
The other way is to measure the resistive flow of a fluid under the weight of gravity. The result is kinematic viscosity.
Put another way, kinematic viscosity is the measure of a fluid’s inherent resistance to flow when no external force, except gravity, is acting on it.
Measuring Kinematic Viscosity
There are several ways to find the kinematic viscosity of a fluid, but the most common method is determining the time it takes a fluid to flow through a capillary tube. The time is converted directly to kinematic viscosity using a calibration constant provided for the specific tube.
The unit of measure of kinematic viscosity is Centistokes (cSt).
A basic difference between the dynamic and kinematic viscosity measurements is density.
Density actually provides a way to convert between a kinematic and a dynamic viscosity measurement. The formula for the conversion is:
- Kinematic (cSt) x Density = Dynamic (cP)
- Dynamic (cP) / Density = Kinematic (cSt)
For a given sample, with a density greater than one, dynamic viscosity will always be the higher number.
Need a Refresher on Density?
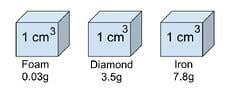
Density is the ratio of the mass (or weight) of the sample divided by the volume of the sample. Think about an ice cube and a cube of steel. They may be the same size, but the steel cube weighs more than the ice cube. Therefore, we say that steel has a greater density than ice cube.
The mass (or weight) of a fluid is determined by gravity. In the kinematic measuring method, gravity is the only force that acts on the sample.
Different viscosities for Vortex Flow Meters
The LIQUI-VIEW Base series operate on the vortex principle.
The obstruction (bluff body) placed in the flow of the liquid sheds vortices downstream at a frequency proportional to the velocity of the liquid.
A piezoelectric sensor detects the vortices and creates electrical pulses which are proportional to the liquid flow rate.
LIQUI-VIEW Base provides the output either with pulse output or analog output (4-20 mA).
The LIQUI-VIEW instruments are able to work up to 1.8 cSt with an accuracy of <2%RD
With a viscosity of 1.8 - 4cSt the measuring accuracy is 3%FS, between 4 - 14 cSt the accuracy will be around 4% FS.
| Liquid | Kinematic Viscosity (cSt) |
|---|---|
Water | 1 |
Honey | 2000-10000 |
| Blood | 2-9 |
Olive oil | 30-60 |
| Mayonnaise | 6250-28000 |
* Viscosity changes with temperature, cSt above is average viscosity
